 |
| Aphaneramma gavialimimus Fortuny, Gastou, Escuillié, Ranivoharimanana & Steyer, 2017 |
 |
| Aphaneramma gavialimimus
Fortuny, Gastou, Escuillié, Ranivoharimanana & Steyer, 2017
|
Abstract
Trematosaurids form a very large and remarkable clade of Triassic tetrapods (Temnospondyli: Stereospondyli) with a worldwide geographical distribution. Compared with specimens from Europe, Australia or North America, they remain relatively scarce in African rocks, where they are mainly known in the Early Triassic of Madagascar and South Africa. Longirostrine trematosaurids were only known from Madagascar, represented by the genus Wantzosaurus. However, we describe herein a new species of the longirostrine trematosaurid Aphaneramma, Aphaneramma gavialimimus sp. nov., from the Olenekian (Lower Triassic) of Madagascar. This genus was previously known from the Early Triassic of Europe and Asia. Based on a new nearly complete skull, the new species is characterized by a premaxilla-nasal suture anteriorly directed, not contacting the nostrils; choanae completely included within the palatines; the ventral opening of the orbits in the anterior part of the interpterygoid vacuities; a very elongated nasal covering more than 50% of the prenarial length; and an anteriorly widened cultriform process. Aphaneramma gavialimimus sp. nov., with a skull length of about 40 cm, may be one of the largest known trematosaurids. Its inclusion in a new phylogenetic analysis confirms its close affinities with the North American genus Cosgriffius, and clarifies the relationships of trematosaurids in general and lonchorhynchines in particular. The new species also increases the palaeobiodiversity of marine trematosaurs in Gondwana and allows discussing their apparently rapid cosmopolitanism just after the great Permian–Triassic mass extinction.
Keywords: Lonchorhynchinae, Olenekian, palaeobiogeography, Permian–Triassic mass extinction
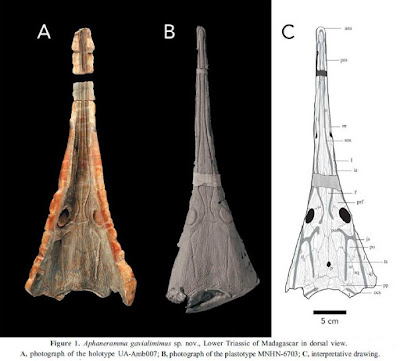 |
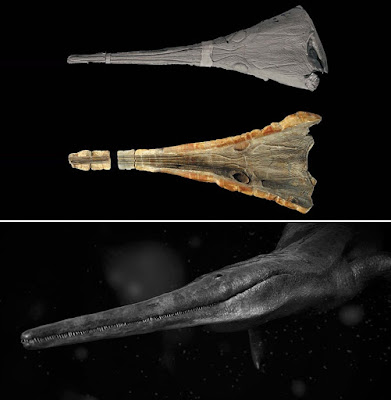
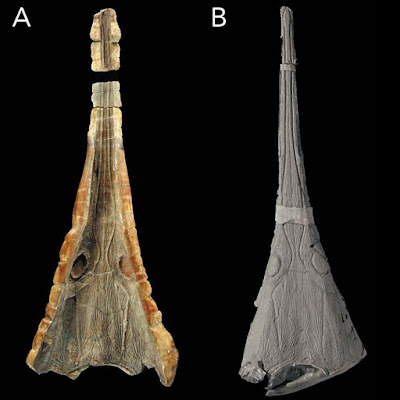
| Figure 1. Aphaneramma gavialimimus sp. nov., Lower Triassic of Madagascar in dorsal view. A, photograph of the holotype UAAmb007; B, photograph of the plastotype MNHN-6703; C, interpretative drawing. |
Systematic palaeontology
Temnospondyli Zittel, 1888
Stereospondyli Zittel, 1888
Trematosauria Romer, 1947 sensu Yates & Warren, 2000
Trematosauroidea Säve-Söderbergh, 1935 sensu Schoch, 2013
Family Trematosauridae Watson, 1919
Subfamily Lonchorhynchinae Säve-Söderbergh, 1935 sensu Steyer, 2002
Aphaneramma Smith Woodward, 1904
Type species. Aphaneramma rostratum Smith Woodward, 1904
(D ‘Lonchorhynchus obergi’ Wiman, 1910) from the early Olenekian of the Sticky Keep of Spitsbergen, Vikinghøgda Formation, Svalbard Archipelago, Norway.
Definition. All taxa sharing a more recent common ancestor with Aphaneramma rostratum than with Cosgriffius campi.
Aphaneramma gavialimimus sp. nov.
Etymology. Imitates a gharial (Gavialis gangeticus), due to the general shape similarity with this hyper-longirostral taxon.
 |
| Aphaneramma gavialimimus sp. nov., Lower Triassic of Madagascar.
Life reconstruction by Marc Boulay (MarcBoulay.fr).
|
Josep Fortuny, Stéphanie Gastou, François Escuillié, Lovasoa Ranivoharimanana and J.-Sébastien Steyer. 2017. A New Extreme Longirostrine Temnospondyl from the Triassic of Madagascar: Phylogenetic and Palaeobiogeographical Implications for Trematosaurids. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. DOI: 10.1080/14772019.2017.1335805



